COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF FMT IN TYPE 1 DIABETIC MICE [PRESENTED AT THE 3RD ANNUAL MEETING OF THE AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OF DIABETES MELLITUS].
On September 23, 2019, the 3rd General Meeting of the Gut Flora Transplantation Clinical Research Society “A Letter to Humanity from Gut Bacteria” was held.
IN THIS ISSUE, WE PRESENT A PRESENTATION BY YOICHIRO OKA, A SENIOR RESEARCHER AT THE INSTITUTE, ON “COMPARATIVE VERIFICATION OF THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS OF FMT IN TYPE 1 DIABETIC MICE”!
From the beginning of the video to around 10 minutes and 15 seconds is the content of this presentation.
background
First of all, in recent years, the development of gene-level analysis technology in the biological field has made it possible to study the intestinal microflora (intestinal flora) of humans in detail. As the intestinal microflora is analyzed, the relationship between intestinal
flora disorder and various diseases caused by a decrease in diversity is becoming clear.
ON THE OTHER HAND, THERE IS FECAL MICROFLORA TRANSPLANTATION (FMT), WHICH MAY CURE THE DISEASE IF THE INTESTINAL FLORA IS IMPROVED.
IN THIS STUDY, WE INVESTIGATED THE THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF FECAL MICROFLORA TRANSPLANTATION (FMT) IN TYPE 1 DIABETIC MICE WITH OUR DEVELOPED ULTRA FINE BUBBLE (UFB)-BASED HUMAN BACTERIAL SOLUTION.
Regulation of blood glucose levels and the mechanism of diabetes mellitus
First, let’s talk about blood glucose regulators.
Let us assume that you are generally healthy. Normally, the balance of blood glucose in the body consists of two main regulators.
The first is the hypoglycemic hormone, which lowers blood glucose levels, and the second is the hypoglycemic hormone, which conversely raises blood glucose levels.
Insulin is the representative hypoglycemic hormone, while glucagon, cortisol, catecholamine, growth hormone, and thyroid hormone are known as hypoglycemic hormones.
Thus, blood glucose (glucose) is balanced (regulated) by these hormones: insulin, the descending factor hormone, and the five ascending factor hormones.

However, it is important to note that blood glucose-elevating hormones are usually not secreted until blood glucose levels fall below 80 mg/dL.
So let’s move on to diabetes.
Diabetes is a disease that causes an increase in the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood, which in turn causes a variety of bad symptoms in the body.
The excessive amount of sugar in the blood must be properly regulated by insulin, but this is caused when insulin, the mainstay of insulin regulation, fails to work. There are
two types of insulin failure: type 1 diabetes, in which insulin is not secreted (not produced), and type 2 diabetes, in which insulin is secreted (produced) but its action is not sufficient.
In recent years, diabetes has also been implicated not only in insulin but also in glucagon, and there is an increase in glucagon secretion before and after meals.
Experiments and Considerations for Type 1 Diabetic Mice

In this study, we artificially created and prepared type 1 diabetic mice with a drug called streptozocin. These diabetic mice were divided into 4 groups of 6 mice each.
THE FOUR GROUPS ARE: GROUP A WITHOUT TREATMENT, GROUP B WITH INSULIN TREATMENT, GROUP C INJECTED ONLY WITH WATER (UFB) THAT WE DEVELOPED, AND GROUP D INJECTED WITH A MIXTURE OF UFB AND HUMAN BACTERIA SOLUTION. THE EXPERIMENTAL PERIOD WAS 14 DAYS.

Measurements. For blood this time, blood glucose was measured at 3 points before transplant, 7 and 14 days after transplant, and insulin was measured at 1 point 14 days after transplant.
Fecal flora analysis is performed at 5 points before and after transplantation on days 2, 6, 12, and 14.
Results of blood glucose and insulin levels
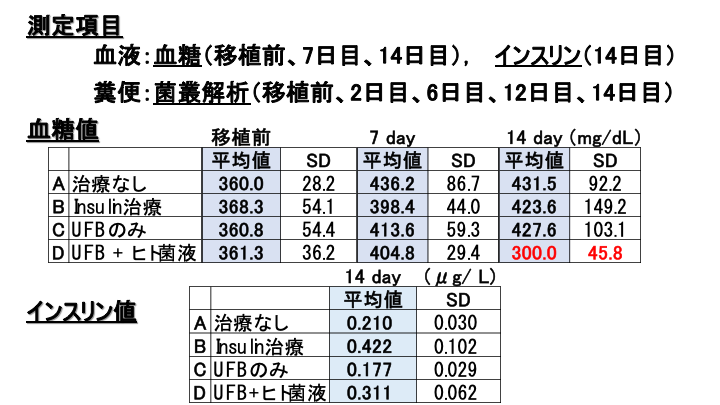
First, here are the blood glucose results. There was no difference between the four groups before and 7 days after transplantation; on day 14, the human bacillus thyroid transplant group had a level 120 mg/dL lower than the other three groups.
Next is the insulin level. The human mycobacterial fluid transplant group had the next highest values after the insulin treatment group.
Results of Bacterial Flora Analysis
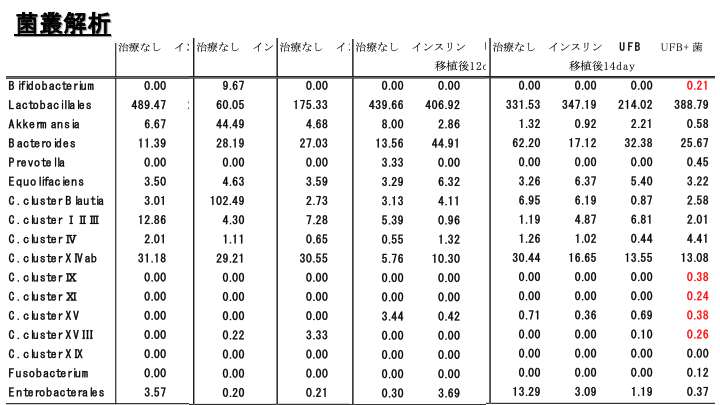
NEXT IS THE BACTERIAL FLORA ANALYSIS. HERE EACH BACTERIAL GROUP IS TABULATED AS A NUMERICAL VALUE OF THE PERCENTAGE OF DETECTION. IN THE VERTICAL COLUMNS, FROM LEFT TO RIGHT, THERE ARE FOUR GROUPS: NO TREATMENT, INSULIN TREATMENT, UFB ONLY, AND HUMAN BACTERIAL FLUID TRANSPLANT GROUP.
BEFORE TRANSPLANTATION, THERE WERE NO DETECTIONS IN BIFIDOBACTERIUM OR THE C CLUSTER AT THE BOTTOM OF THE TABLE IN ALL FOUR GROUPS.
Day 2 after transplant. Bifidobacterium is seen in the bacterial solution transplant group, although it is also present in the no treatment group.
Day 6. The human fungal fluid transplant group shows an increase in detection of the group of bacteria in the red area compared to the other three groups.
Day 12. The red area of the human fungal transplant group is maintained.
Day 14. The detection of the red area of the bacteria group did not change.
Key Result
Blood glucose levels were approximately 120 mg/dL lower in the human bacterial fluid transplant group.
Insulin levels were found to be the second highest in the human mycobacterial fluid transplant group after the insulin-treated group.
Bacterial flora analysis showed diversity in the flora in the human mycelial explant group.
Consideration -Why did blood glucose levels drop?
The reason why blood glucose levels were suppressed in the diabetic mice transplanted with human mycelial fluid is as follows. First of all, the diabetic mice do not produce insulin because they have type 1 diabetes.
First of all, the diabetic mice are type 1 diabetic, so they do not produce insulin.
So why did blood glucose levels drop?
We associate diabetes with high blood sugar and insulin administration, which equals blood glucose-lowering hormones, but in fact, there is already a recent medication other than insulin that can control blood glucose levels.
It is not exactly that what I am about to introduce is directly medicated. It is that it may be related to the function of the factor.
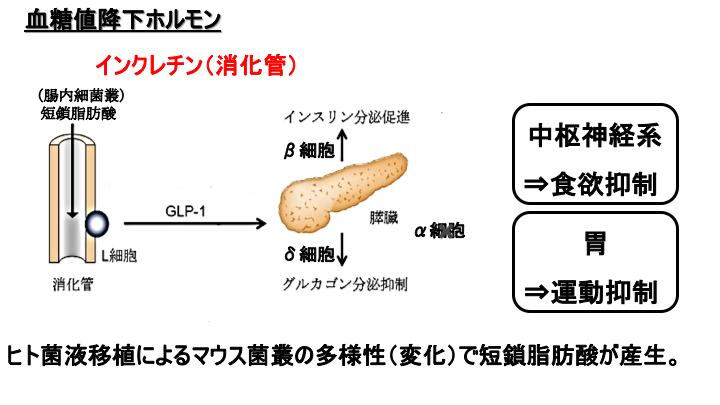
It is the hormone incretin , which is secreted from the gastrointestinal tract. Incretin is a short-chain fatty acid produced by intestinal bacteria in the intestinal tract that acts on L cells to secrete a hormone called GLP-1.
In fact, in addition to GLP-1, there is another hormone called GIP, which is the generic name for incretin. I will omit the discussion of GIP this time. GLP-1 secreted
from L cells acts on the pancreas to promote insulin secretion and suppress glucagon secretion.
GLP-1 ALSO ACTS ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM AND STOMACH, CONTRIBUTING TO THE SUPPRESSION OF ELEVATED BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS.
The reason why the blood glucose levels were lower in this study than in the other three groups may be due to the production of short-chain fatty acids as a result of changes in the diversity of the mouse bacterial flora caused by the transplantation of human bacteria fluid.
summary
THE FOLLOWING OBSERVATIONS WERE MADE IN THIS UFB+HUMAN MYCELIUM TRANSPLANT GROUP.
1. Inhibition of elevated blood glucose
2. Insulin levels were the second highest in the insulin treated group
3. Diversity in bacterial flora was observed
In this study, we found that FMT had a suppressive effect on blood glucose elevation in type 1 diabetic mice.
On the other hand, we could not elucidate the mechanism of this effect due to the lack of sufficient test items that must be measured.
We would like to conduct additional studies in the future to clarify its hypoglycemic effects.
From the beginning of the video to around 10 minutes and 15 seconds is the content of this presentation.
その他の Blog に関する記事
Articles about other Blog

October 26, 2021
WHAT IS THE GOAL OF FMT? IMPACT OF NUMBER OF TRANSPLANTS AND PRIOR ANTIBIOTIC ADMINISTRATION ON BACTERIAL VIABILITY
Effect of Number of Transplants and Prior Antibiotic Administration on Bacterial Engraftment Original Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Engraftment of Bacteria after Fecal Microbiota Tra […].

August 03, 2021
Timing of intestinal bacteria to the inside of the mucosa
Conventional wisdom is that intestinal bacteria are only found in the outer mucus layer. The intestine is a hose-like cavity that serves as a pathway for bacteria, food, and water. The inside of the hose is not suddenly the cells of the large intestine, but the mucus and mucous layer separates the outside from the inside. The mucus layer […].
May 31, 2021
FMT IS EFFECTIVE AGAINST PARKINSON’S DISEASE AND RESISTANT BACTERIA [2021.5.31].
FMT relieves symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (Original) Evaluation of fecal microbiota transplantation in Parkinson’s disease patients wit […].




