WHAT IS THE GOAL OF FMT? IMPACT OF NUMBER OF TRANSPLANTS AND PRIOR ANTIBIOTIC ADMINISTRATION ON BACTERIAL VIABILITY

Effect of number of transplants and prior antibiotic administration on bacterial viability
Author:Taylor S. Cohen Vancheswaran Gopalakrishn
Affiliation: Microbiome Discovery, Microbial Sciences, BioPharmaceuticals R & D, AstraZeneca, Gaithersburg, Gaithersburg, MD 20878, USA
Information from Biologics Research and Development, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals of America, Inc.
Paper Abstract
SPF mice were used for FMT establishment studies.
*SPF mice…mice that do not harbor mouse-specific pathogens
Two antibiotic pre-treatments were administered for 3 days and 3 weeks, followed by one or five FMTs of human origin, and stools were followed by 16S rRNA sequencing (so-called next-generation sequencing) over a long period.
Diversity was restored faster in the 3-day antibiotic group, whereas the group that achieved results similar to the donor gut microbiota was the group that received 3 weeks of antibiotics followed by 5 FMTs.
Background and Objectives
As you know, intestinal bacteria play an important role in the host’s immune system and many diseases have been reported to be caused by disturbances in the balance of these bacteria.
In this situation, a method called FMT (fecal transplantation or intestinal flora transplantation) is being tested to restore the intestinal flora imbalance (dysbiosis), and clinical trials are being conducted for a wide range of diseases from Clostridium Difficile infection to cancer and ulcerative colitis.
Animal studies are naturally conducted prior to human clinical trials, but there are many barriers to testing FMT in sterile mice.
For example, sterile mice do not have normal function of immune mechanisms such as B cells, T cells, and IgA, and their intestinal mucus layer is immature, so the effects on disease may not be well observed, and in this experiment, SPF is used. mice, which have bacteria but do not harbor mouse-specific pathogens.
Furthermore, the main purpose of this experiment is to test various aspects of “bacteria fixation by FMT,” which has not yet been established, such as preadministration of antibiotics and the number of times of FMT.
method
At six weeks of age, the mice were divided into the following six groups. Five mice were assigned to each group, for a total of 30 mice.
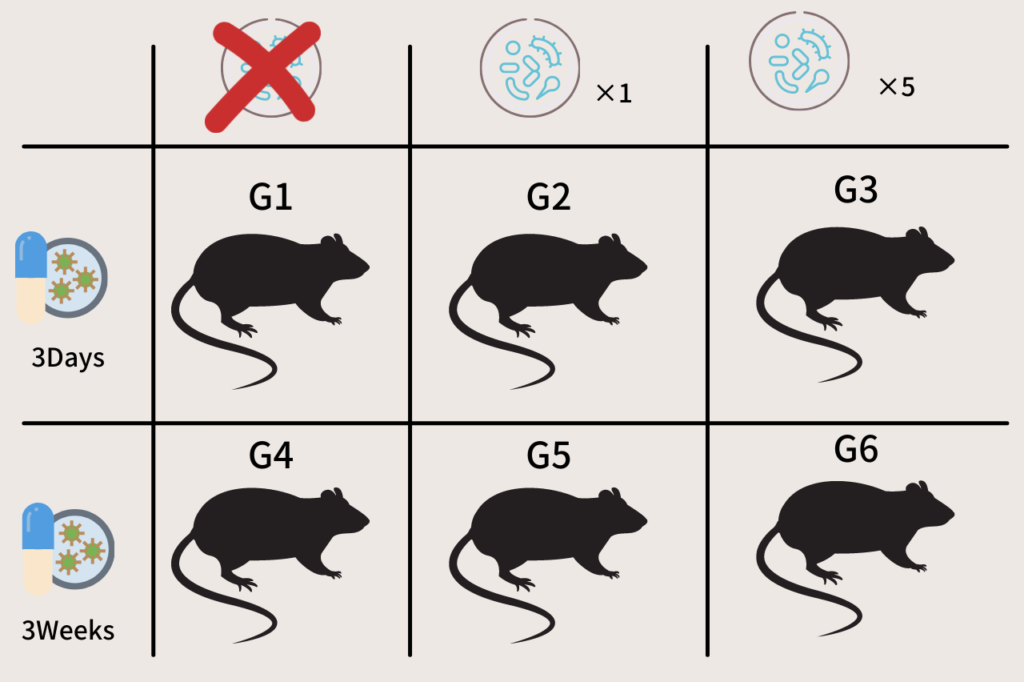
The images are handmade, so please tolerate slight misalignments.
G1:3 days antibiotics, no FMT
G2:3 days antibiotics, 1 FMT
G3 : 3 days antibiotics, 5 FMT
G4:3 weeks antibiotics, no FMT
G5:3 weeks antibiotics, 1 FMT
G6 : 3 weeks antibiotics, 5 FMT
Intestinal flora analysis and measurement of metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids were performed on 30 mice at each of the following points
T0:first
T1:after antibiotics, before FMT
T2:after antibiotics, immediately after FMT
T3: 1 week after FMT
T4: 2 weeks after FMT
T5: 3 weeks after FMT
All FMT is done between T1 and T2.
result
The results of the experiment are described from three perspectives: restoration of diversity, establishment of human bacteria, and types of bacteria that have increased.
Degree of diversity restoration

DURING THE T1-T2 PERIOD AFTER ANTIBIOTIC TREATMENT, THE DIVERSITY OF INTESTINAL BACTERIA DECREASED IN ALL MICE, BUT THEY ALL BEGAN TO RECOVER DURING THE T2-T5 PERIOD.
Mice in the G1-G3 group generally recovered their original diversity, rather than the diversity of the transplanted human donors.
Mice in the G4-G6 group, on the other hand, remained at low diversity even at T5.
See figure A in Figure 2 for details.
The order is G1 and G2 > G3 > G6 > G4 and G5
, with little change in the G4-G6 mice.
The G1-G3 mice are given antibiotics for 3 days. The G4-G6 mice received antibiotics for 3 weeks, seven times longer than the G1-G3 mice. This shows that diversity was lost due to antibiotic treatment.
Degree of human fungal colonization
Amplicon sequence variant (ASV) is a term used to refer to single DNA sequences recovered from a high-throughput marker gene analysis. These amplicon reads are created following the removal of erroneous sequences generated during PCR and sequencing. This allows ASVs to distinguish sequence variation by a single nucleotide change.
Amplicon sequence variant – Wikipedia
(A term used to refer to a single DNA sequence recovered from a high-throughput marker gene analysis. These amplicon reads are created after removing erroneous sequences generated during PCR and sequencing. This allows ASV to distinguish sequence variation by a single nucleotide change).
If you read the paper, it makes some sense.
ASV seems to be able to determine “this is human bacteria” and “this is mouse bacteria” at the genetic level.
IN THE EXPERIMENT, ASVS IN THE TRANSPLANTED BACTERIAL FLUID ARE HUMAN ASVS, AND ASVS FOUND ONLY IN MICE BEFORE TRANSPLANTATION ARE MOUSE ASVS.
RESULTS SHOWED THAT IN A COMPARISON BETWEEN G3 AND G6 MICE, BOTH HAD MORE HUMAN ASV IN THE T3 PHASE AND G6 MICE HAD MORE HUMAN ASV (73 VS. 28)
AS FOR THE RE-EXPRESSION OF THE MICE’S OWN ASV DURING THE T2-T5 PHASE, 75% AND 50% IN THE G2 AND G3 GROUPS, RESPECTIVELY, COMPARED TO ONLY 25% IN THE G6 GROUP.
Let me restate the earlier information here.
G1:3 days antibiotics, no FMT
G2:3 days antibiotics, 1 FMT
G3:3 days antibiotics, 5 FMT
G4:3 weeks antibiotics, no FMT
G5:3 weeks antibiotics, 1 FMT
G6 : 3 weeks antibiotics, 5 FMT
T0:first
T1:after antibiotics, before FMT
T2:after antibiotics, immediately after FMT
T3: 1 week after FMT
T4: 2 weeks after FMT
T5: 3 weeks after FMT
All FMT is done between T1 and T2.
Type of bacteria increased
Firmicutes (especially Lachnospiraceae) are bacteria that are commonly found in human donors. Firmicutes is one of the phyla of bacteria.
By the way, a phylum is the top level of a taxonomic class. Bacterial domains are classified into phylum, class, family, order, genus, and species, and belonging to a new phylum, for example, indicates that the bacterium is phylogenetically highly novel. https://qr.paps.jp/zFNOb (Source: National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology)
It is speculated that the human-derived Bacteroides gate stimulated and restored the mouse’s own Bacteroides gate, which was thought to have disappeared due to antibiotics. It is speculated that this may be the case.
What does it mean to “settle down?

THE CONCLUSION OF THIS PAPER IS THAT PERFORMING FMT MULTIPLE TIMES AND ADMINISTERING PRIOR ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY MAY BE A USEFUL OPTION IN KEEPING THE BACTERIA VIABLE.
Now, let me take a moment to consider the meaning of the word “established” here.
What is shown in this experiment is fixation based on the evaluation axis of “how much of the transplanted human donor’s bacteria remains after transplantation”.
The hypothesis is that by repopulating the donor gut with donor gut bacteria, the intestinal flora balance can be restored and health restored.
The conclusion of this paper is, in other words,
“If you want to erase the gut flora that the recipient (in this case, the mouse) originally has and replace it with the gut flora balance of the donor, this method works.
Our Approach to Transplantation

If you perform FMT using our method, the conclusion will be different. Although the suppression of bacteria by chemicals may be effective temporarily, in the long term, the negative effects will be greater, as typified by the phenomenon of bacterial replacement. Our FMT is expected to be effective in “fusion and symbiosis” rather than “species distinction,” so it is out of concept in the sense of “FMT to expand the area of establishment.
Some universities are approaching other universities and countries with ideas like the paper in question, and although it may be difficult, we believe that it is urgent for us to become an academic group that is recognized around the world.
I see you have a new word: “FMT that expands the area of fixation.”
What am I going to do now that it’s just a long blog?
Briefly, the Firm’s bacteria solution is NanoGAS™, which is a nanobubble water.
Patients’ intestines often have fewer places for bacteria to live.
The concept is that by using NanoGAS™ as a solvent, we can physically increase the number of places for bacteria to live in the intestines, rather than “eliminating” other bacteria like antibiotics.
I wrote this in a nutshell, but I am confident in what I am doing.
There are many different methods of FMT, and one day a “standard method” will be established.
I hope that methods that make patients feel better and happy both in the short and long term will be properly and justly evaluated.
その他の Blog に関する記事
Articles about other Blog

October 26, 2021
WHAT IS THE GOAL OF FMT? IMPACT OF NUMBER OF TRANSPLANTS AND PRIOR ANTIBIOTIC ADMINISTRATION ON BACTERIAL VIABILITY
Effect of Number of Transplants and Prior Antibiotic Administration on Bacterial Engraftment Original Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Engraftment of Bacteria after Fecal Microbiota Tra […].

August 03, 2021
Timing of intestinal bacteria to the inside of the mucosa
Conventional wisdom is that intestinal bacteria are only found in the outer mucus layer. The intestine is a hose-like cavity that serves as a pathway for bacteria, food, and water. The inside of the hose is not suddenly the cells of the large intestine, but the mucus and mucous layer separates the outside from the inside. The mucus layer […].
May 31, 2021
FMT IS EFFECTIVE AGAINST PARKINSON’S DISEASE AND RESISTANT BACTERIA [2021.5.31].
FMT relieves symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (Original) Evaluation of fecal microbiota transplantation in Parkinson’s disease patients wit […].




